Having a car comes with a lot of responsibilities. They are highly demanding, high-performance equipment that necessitates constant attention and service, particularly engine maintenance. Your oil should be changed every 8,000 to 15,000 miles, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. In reality, simply changing your car’s oil can help your engine last longer. Otherwise, here you can find out how to fix a seized engine.
While there are many other vital things to do to maintain your car’s engine, keeping the oil level can make a major difference between requiring a few fixes and needing a complete engine replacement. Failure to change your oil regularly can cause internal damage. The most dangerous is an engine seizure. In this article, we’ll go through the signs and symptoms, as well as how to fix a seized engine.
- What Is A Seized Engine?
- Reason For Seized Engine
- What Are The Symptoms?
- Retrieve A Locked Engine
- Fixing A Seized Engine?
- FAQs
When An Engine Is Seized, What Does That Mean?
When your car’s engine is seized, it won’t start. Your electronics may function normally, but your engine will not start, and the vehicle will not move. When you try to start the engine, it instead makes clunking noises.
A seized engine can have various causes, but the most common one is a lack of lubrication. This is important for us to learn in understanding how to fix a seized engine.
Oil lubricates the piston, allowing it to travel effortlessly within the cylinders. Metals would otherwise scrape against each other, releasing a significant amount of heat. An engine will seize as a result of this.
What Is The Reason For An Engine That Has Seized?
Before you can start fixing your engine, you must first figure out what caused it to lock up in the first place. A lack of lubrication, a lack of circulation, or a lack of use are the three most common reasons for an engine to seize. However, those are just the oil-related ones; there’s also hydro-lock and vapor lock to think about.
The Following are the Causes of Engine Seizing:
A Scarcity Of Oil
Your engine will eventually seize if there isn’t enough oil in it. This is because oil forms a thin barrier between the cylinder walls and the pistons, allowing them to move without overheating.
If you remove that layer, you’ll have metal grinding against metal, resulting in much friction and heat. Consider rubbing your hands together fast, then doing the same thing when moist.
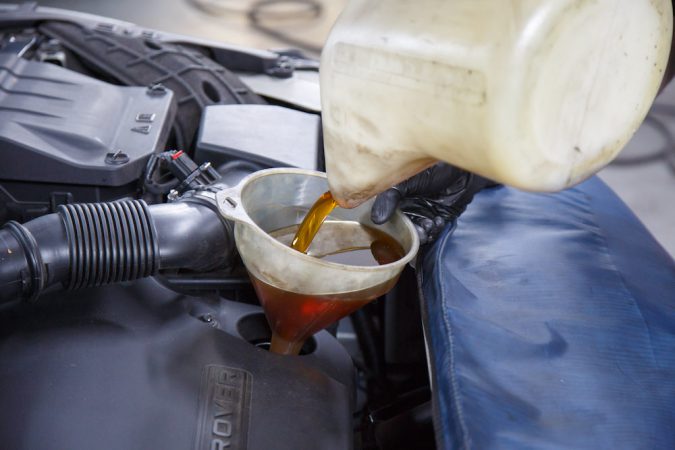

This will eventually harm the crank bearings, rod ends, and main caps, all of which are your engine’s essential components. The rods may also fuse to the crank, causing the pistons to “blow” out the side of the block. You’re looking at a hefty repair expense in this situation.
However, if you stick to the manufacturer’s service schedule and change your oil regularly, you should be able to prevent this problem entirely.
The Following are Signs that your Engine is Low on Oil:
- The smell of burning oil
- Overheating of the engine
- Indicator of oil pressure
- Sounds of knocking and clunking
- A decrease in performance
Circulation Issues
In the same way, engine seizing can be caused by oil running out, the same thing can happen if oil isn’t being circulated in the first place. The oil pump is in charge of “pumping” oil from the gas tank to the numerous components that require it. Your engine may seize if it fails.
The Following are Signs that your Oil Pump is Failing:
- The temperature rises in the engine
- The engine makes a loud “tapping” sound.
- Indication of oil pressure
It’s critical to detect a broken oil pump as soon as possible. This is the difference between a $300 and a $3,000 repair expense (or more). Similarly to the primary cause, changing your oil regularly is necessary for your oil pump to remain in good working order. The oil filter also removes hazardous particles such as dirt, dust, and metal from the engine before their entry.
Lack Of Utilization
Is it possible that you’ve ever sat for so long that your muscles ache and your joints were sore as a result? It’s also possible for an automobile engine to corrode if it’s been sitting for too long without being used.
When rust builds up inside the cylinders, the piston rings can become stuck in place. How can you tell if your engine has seized due to inactivity? The engine may have locked if the inside lights are on, and you can crank the key in the ignition, but the engine won’t start.

An electrical short in the starter is another possibility when the engine cannot be started. If you turn the key and a little smoke cloud comes from under the front of your automobile, you may have a seized engine as well as a faulty starter.
The good news is that all of this may be avoided by simply starting the engine once a month or so. To be extra safe, check for leaks as well; this will help you avoid the most common cause of a seized engine, a shortage of oil.
Locked In By Water
When an engine gets hydro-locked, what does that mean? Pistons in engines are made to compress a mixture of air and fuel, not water. As a result, if enough water enters the cylinder, it may be a hydro lock, which means it will all stop moving simultaneously.
Much of the harm is determined by how fast you were traveling at the time. The most important thing to do if you have a locked hydro engine is to take care of it as soon as possible before it rusts or causes harm to the cylinders.
Vapor Locking Mechanism
While vapor lock isn’t as often as the other reasons for your engine locking up, it does happen. Vapor lock occurs when the liquid inside your fuel system grows too hot, forcing it to turn into a gas, which your engine isn’t designed to handle.
The vapor lock may be causing your engine to splutter and eventually lose power. It’s more common on older cars, especially those exposed to the sun over an extended period of time.
Rusted Components
Metal is prone to corrosion over time—the likelihood of rusting parts increases as the vehicle ages. While appropriate lubrication prevents internal engine parts from rusting, it is possible that water could sneak inside. When parts rust, the components grind together, resulting in metal shavings that might obstruct functioning.
Components That Are Broken
Movable parts are not impervious to corrosion. It’s also conceivable for parts to collapse. The cylinders, connecting rod, or pistons are all affected. A broken part will become lodged in the engine and clog the system. This is what is known as the cumulative effect, in which one flaw leads to another.

Engine Is Overheated
It would be best if you never let the engine overheat. Otherwise, you’ll have major problems. To begin with, overheating engines cause pistons to expand, potentially damaging the cylinder walls. Aside from that, when the engine overheats, you can blow a head gasket, which is an expensive repair.
Starter Locked
While a locked starter does not cause a seized engine, the symptoms are quite similar. The two can share the same feelings. When the starter seized due to a stuck solenoid, the flywheel was grabbed. Fortunately, this is a far more manageable repair than a seized engine.
Camshaft/Timing Belt Breakdown
The valves can impact the pistons if the timing chain, belt, or camshaft fails. Problems with the pistons cause the engine to seize, as we’ve already discussed.
What Is The Difference Between A Seized Engine And A Dead Battery?
When an engine doesn’t start, many people assume the problem is with the battery. In some cases, this is correct. If you leave your headlights on overnight or a door isn’t completely shut, the battery will be drained, rendering your car unworkable.
What distinguishes a dead battery from a seized engine is what does and does not work. Your automobile won’t start if your battery is dead, and neither will the electronic components. On the other hand, if your engine has seized, the electronic components may still function, but your automobile will not start.
How To Fix A Seized Engine – Signs And Symptoms
The symptoms of a seized engine come in two stages. The first is when the engine is on the verge of seizing up, and the second is when it seizes completely.
Early Symptoms
- When the engine is running, there is a mild knocking or tapping sound caused by the piston rod colliding with the crankshaft in the early stages of the problem. The sound gradually becomes a loud knocking known as the ‘dead-knock.’
- The dashboard warning light for the check engine or check oil is also a warning symbol.
- When the engine is idling, it makes strange noises like the air is leaking at every stroke.
- When you start the engine, it makes a constant grinding noise.
- Excessive engine oil consumption and continuously low engine oil when you check.
- The odor of overheated oil.
- Abnormally severe shaking of the engine, usually caused by a bent crankshaft.
- The engine begins to function poorly, which is a common indicator of leakage beyond the piston seals.
Signs That Your Engine Has Seized
- A broken piston rod has pierced the engine block.
- When the crankshaft breaks and the engine stops running, a loud breaking sound is usually heard.
- Even with a full tank of gas, a completely charged battery, and new spark plugs, the engine would not start, although all battery-powered devices work fine. This usually occurs when the piston becomes stuck within the cylinder.
- Finally, the mechanic gives his feared verdict: “The engine is dead.”
How To Retrieve A Locked Engine
Now that you know what causes a locked engine, you might be wondering how to fix a seized engine. Depending on the cause, a seized engine repair may be possible. The bad news is that a seized engine owing to a lack of oil is nearly impossible to liberate.
If this is the case, releasing a stuck engine may necessitate replacing various parts or the entire engine in the worst-case scenario. Oil deficiency causes lasting damage to engine components. You may have to salvage your car or sell it to a trash car buyer as a final resort.
You’ll have to wait for the engine to cool down if it’s seizing due to vapor. This permits the gas to revert to a liquid state. Another alternative is to spray the fuel pump with water. You may have to pay for a replacement if an engine freezes due to moisture.

There may be too much rust if your engine has seized after sitting for too long. Fixing this without spending a lot of money is challenging. Repairing won’t work if the majority of the pieces are rusty. Your car’s engine will need to be replaced. You may be able to save your engine if you contact a mechanic as soon as you notice symptoms.
Now how to repair a seized engine of a car? For that, you’ll need the following tools and materials:
Required Tools:
- Combination wrench set
- Bar breaker
- A set of screwdrivers (Both standard and Phillips)
- A single socket set
Required Materials:
- Sealant for gaskets
- Masking tape and a pen
- An oil that penetrates
- A few gaskets to replace
How to Fix A Seized Engine Due To Rust In 5 Easy Steps
Unplug All Of The Fittings
The crankshaft drives the majority of the parts outside of the engine unit. Disassemble all belt-driven accessories as well as the under-hood components. The power steering and water pump, as well as the alternator, caused the crankshaft to drag. The power required to eject the piston and turn the crankshaft can be lowered by detaching the aforementioned pieces.
Ensure Pressure Is Equalized Throughout The Engine
To begin, use a socket to remove the spark plugs. Mark numbers on the wires you’re disconnecting at the same time, so you don’t get lost while reconnecting each wire to its cylinder. They may release pressure against you as you strive to remove the piston. The pressure can be relieved by removing the plugs.
Take Off The Valves Covers
You’ll need a wrench to loosen all restraining nuts that keep the valve cover on each cylinder in place. The rocker arms will be visible after the cover is removed. Remove the rocker arms by unscrewing each nut that holds them together. Pull the exposed rods from the cylinder head with force. You may overcome the resistance and turn the crankshaft by hand in this manner.
Crankshaft Rotation
Locate the engine assembly’s front side. Any transverse engine’s front side can be found on one of the two sides. A pulley-driven belt or disk-like harmonic balancer can be found on this site.
A bolt head is located in the center of both of these components. Attach a socket to the middle bolt with a long-handled breaking bar. By rotating this bolt clockwise, you can free the engine.
If you’re having trouble turning the engine, use the spark plug assembly to apply penetrating oil to the cylinder walls. Allow the engine to run for a few hours without being disturbed to remove the parts quickly.
This method may necessitate the use of multiple applications to produce results.
If your car has a manual transmission, use stick shifts to change gears, move the car around, and utilize thrust to crank the engine.
Reassemble All Of The Components
Reassemble all of the pieces carefully now that your engine is free and oiled. Recharge your battery and attempt to start your car again. If the engine still doesn’t start following this procedure, the issue must be more severe than cylinder rust. You must now drive your vehicle to the nearest service center and save it!
Is It Possible To Rebuild A Seized Engine?
There’s always the option of rebuilding an automobile engine, but labor expenses can quickly mount depending on the issue. Before providing an estimate, the mechanic will need to disassemble the engine to check for irreversible damage. The mechanic will not want to witness a rod go through the engine block for the most part.
Furthermore, if the engine has overheated, interior components may have deformed, reducing the engine’s durability. In most circumstances, it’s simply more cost-effective to replace the engine.
How Much Does It Cost To Fix A Seized Engine?
Whether you replace it or rebuild it, the cost of repairing a seized engine will quickly approach $3,000. This expense probably won’t matter if you have an older vehicle, which is why many automobiles with seized engines eventually end up in the junkyard.
Seized Engine vs Malfunctioning Starter
A seized engine is sometimes mistaken for a bad starter. Because the solutions to various difficulties vary, it is critical to diagnose the problem appropriately. A locked starter can cause the same symptoms as a frozen engine.
Mechanics can tell the difference between the two by spinning the crankshaft manually. This helps to rule out the starter as a source of engine issues. If the crankshaft can be manually spun, the starter is most likely the source of the problem. The starter is removed if the crankshaft cannot be moved, and another effort is made.
Is It Possible To Prevent A Car Engine From Seizing?
The good news is that an engine can be prevented from shutting down. This is a lot less expensive than trying to start a locked motor. It all comes down to maintaining your vehicle regularly. The most important thing is to change your oil regularly. That’s because a lack of oil in the engine is the most common cause of engine lockup.
Avoid driving through puddles since the water will damage your engine. If there is a flood, try to lock your engine so that water does not enter it. Avoiding long periods of exposure to the sun is another strategy to prevent seized engines. In addition, attempt to drive your automobile as frequently as possible to prevent engine rust.

In any event, keep an eye on what’s going on with your car. Keep an ear out for unexpected noises or smoke coming from the engine. Call a mechanic as soon as you discover a problem. Early detection of an issue can save you a lot of money.
Facts about Seized Car Engines:
- Maintaining the oil levels in your car can help extend the life of your car engine, as failure to do so can lead to internal damages and engine seizure.
- Seized engines and dead batteries are often mistaken for each other. When the battery is dead, the electronic components will not work, but when the engine is seized, they might still work.
- Before an engine completely stops working, there are several indicators that it will or may seize soon, such as a check engine light or a knocking/clunking sound.
- Causes of engine seizure include insufficient oil level, accumulation of water, accumulation of rust, and faulty parts.
- Symptoms of a seized engine include loud cranking/clunking sounds, visible pistons, fumes/smoke, and nothing happening when trying to start the car.
- Most engine failure is due to poor maintenance, specifically a lack of oil in the engine.
- There is debate as to whether conventional or synthetic oil should be used in a car, as each has benefits and drawbacks.
- If a mechanic diagnoses an engine as seized, a complete replacement may be suggested rather than attempting a repair, depending on the severity of the damage.
- Engine rebuild is an option some mechanics can offer, where the engine is rebuilt from scratch rather than repairing the damaged parts.
- The cost of replacing an engine can range from $2,250 to $4,000, or approximately 10% to 20% of the cost of a new vehicle.
How To Fix A Seized Engine – Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some popular FAQs:
Q1. Do A Motor And An Engine Have Any Differences?
Ans: No, the terms engine and motor are interchangeable in the context of automobiles.
Q2. Is It Essential To Replace An Engine?
Ans: Since the level of the damage to your engine will determine the answer, there is no definitive yes or no answer. If a competent mechanic from a respectable company decides that repairs will suffice, replacing your engine may be a waste of time and money. This is something you should talk to a mechanic about.
Q3. How Much Does An Engine Replacement Cost?
Ans: Car owners should budget between $2,250 and $4,000 to replace their engine, which is around 10% to 20% of the cost of a new vehicle.
Q4. What Does It Signify When An Engine Is Seized?
Ans: The radio, A/C, and other electronics in your vehicle may still work with a seized engine, but the engine will not turn over. A knocking or clunking noise may be heard instead.
Final Verdict – How to Fix a Seized Engine
You must have concluded by now that engine faults are the absolute last thing you want to deal with and how to fix a seized engine. Engine repair can quickly drain your bank account. When your car’s engine needs to be replaced, it can be incredibly costly. If you want your vehicle to function smoothly for a long time, you must take care of it.
Ensure you don’t forget about routine maintenance, oil changes, getting the oil filter cleaned, and moving your car every month or so. Take your car for a test drive to ensure that the engine is in perfect working order.
Carefully read the owner’s manual and follow the helpful advice while avoiding the bad. Also, avoid going on water-filled roads because your automobile will become hydro-locked due to the water. Flooded roads should be avoided at all costs, not only to protect your engine but also to keep yourself safe.


