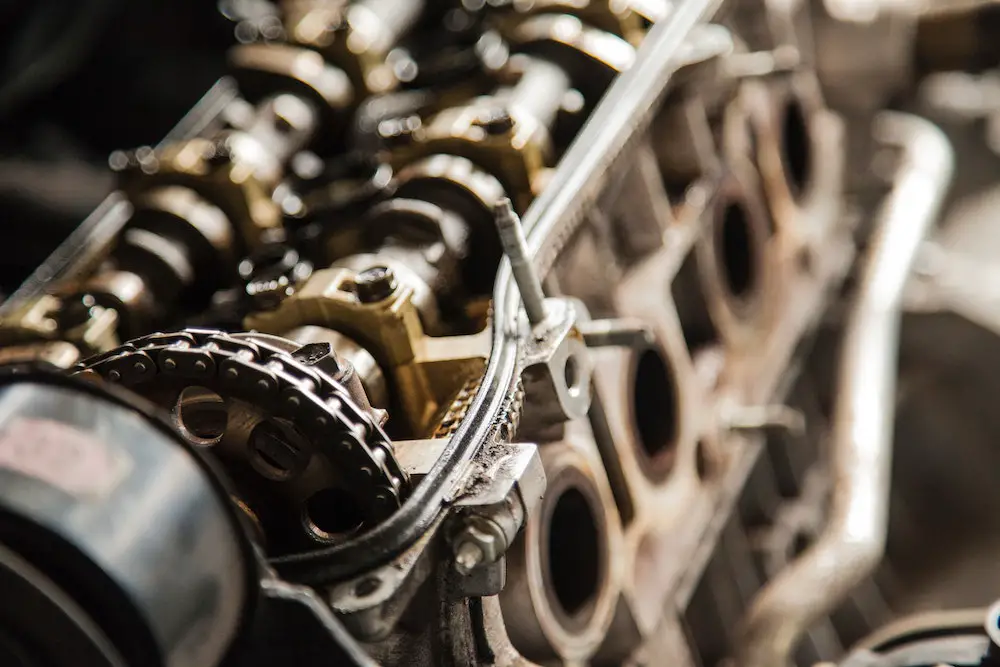
You should never want to hear rod knock sounds coming from your engine. It’s because fixing it will usually cost a lot of money. What is rod knock, what are the symptoms of rod knock, and how can you tell if your engine has it?
You might begin to detect rod knock, a terrifying engine noise, as your car idles. You might feel your heart stop as you think about the pricey engine repairs because it frequently sounds like a loud banging sound. Rod knocks are not present in every engine knock, though.
What is rod knock, what causes it, and how can you recognize the signs of this engine issue?
- Rod Knock
- Rod Bearing Replacement Cost
- Rod Knock Symptoms
- Fixing Rod Knock
- Engine Knocking Causes
- Frequently Asked Questions
Rod Knock
Rod knock occurs when one or more of your rods “knock” against the crank as it rotates in a different direction.
The connecting rod, which we’ll refer to as the rod from now on, connects to the crank, and between the two is a bearing constructed of a material that is softer than the rod or the crank. For the bearing to the surface of the crank journal, there are gap tolerances (measured in 0.001-inch increments) when the engine is constructed.
This tiny opening lets oil flow through and stay on the bearing surface. Between the two surfaces, this oil film creates a barrier. Symptoms of rod knock develop as a result of the oil’s failure to provide a sufficient barrier as the bearing ages and this gap widens.
However, premature rod knock can also result from damage to the bearing or crank journal, which can happen much sooner than normal wear (which can take hundreds of thousands of miles). Your day can take a drastic turn by several issues, including low oil pressure, dirty oil, and loss of oil pressure.
Rod Knock Sound
Rod knock is an internal engine tapping sound that usually gets louder as you go faster or when you put more strain on the engine.
Of course, there are a lot of things that can sound like rod knock (see list at bottom), but if the noise you are hearing is rod knock, you need to know what you are dealing with.
It’s probably not a symptom of rod knock, so check your exhaust gaskets and other potential sources if the knocking noise disappears after the engine warms up.
Rod Bearing Replacement Cost
Depending on whether you hire a mechanic or do it yourself, the cost to replace a rod bearing on average will range from between $20 and $5,000.
The cost will be based on the average costs nationally for all cars and doesn’t account for any fees, taxes, or even your specific model. Additionally excluded are any additional fixes or upkeep like flushing the cooler and engine lines, replacing seals, gaskets, connecting bearing rods, as well as cylinder head bolts.
Visit the RepairPal Fair Price Estimator for an even more precise estimate that is based on your specified make and model.
You will pay between $2,000 and $5,000 at the mechanic.
- Parts: $20-$3,000
- Workforce: $800 to $2,000
When the crankshaft and/or pistons are removed from the engine or during an engine rebuild, rod bearings should be replaced. Both of these tasks can require up to eight hours of labor or more. The engine block may be severely harmed by a failed connecting rod bearing, necessitating a new engine block rather than being able to rebuild the old one.
DIY price range: $15–$3,000
Required Parts:
- Hammer
- Screwdriver
- Rod bearing
- Lint-free towel
- A Press
- An Engine assembly grease
You can save money on the cost of the replacement rod bearings if you know how to disassemble and reassemble an engine yourself because the parts and materials are fairly cheap.
Nevertheless, additional gaskets and seals need replacing for reassembly whenever the engine is disassembled and the crankshaft taken out.
Always remember that rod bearings, seals, gaskets, and other engine parts are constructed for particular models. In case you choose to perform this repair yourself, be sure to buy the proper components for your car. For specifications and manufacturer-recommended parts, if you are not sure, take a look at your owner’s manual.
Why Replace Rod Bearings
Contrary to the ball bearing, which has tiny balls that rotate, the rod bearing is usually a plain bearing that rotates the connecting rod while the crankshaft is spinning using only friction and oil supply.
Via a pinhole that is close to the top, the rod bearing’s interior is accessible to lubricant. Reduced friction inside the bearing also enables free rotation of the crankshaft.
What Does Replacing A Rod Bearing Entail
Your engine’s rod bearings will be a critical component, so you might want to think about hiring a qualified expert to replace these essential parts.
To prevent harm to the engine’s components, take all the necessary precautions if you’ve got the mechanical know-how to complete this project on your own. For you to separate the connecting rods from the crankshaft for replacing the rod bearing, you will need to extensively disassemble the engine.
To prevent mismatched connecting rods and bearing end caps, it is crucial to keep them together. Once you reach this stage, the bearings are simple to take out and reinstall. Avoid removing the bearing with any metallic tools, as you risk damaging the end cap or connecting rods.
Cleaning the surfaces of the bearing with a lint-free cloth is a good idea because debris as well as dirt can lead to failure of the bearing. Once you’re ready to do so, slide one bearing in the end cap with one into the large end of the rod.
For proper oil pressure, the notches on the ends of bearings must be set up opposite each other. For the bearings to prevent loose play, they must also fit firmly inside the connecting rod.
The small end of the rod’s bearing should be pushed out using a press. Tighten the bolts after attaching any new rods to the crank.
Replace the wrist pins and rods attached to the crankshaft and pistons using engine assembly lube. Ensure to tighten everything to the manufacturer’s precise torque recommendations.
What If You Don’t Replace Your Rod Bearing
The friction that is between the engine’s motors and engine bearings will disappear if you don’t replace your rod bearings. At worst, the lack of friction may result in the connecting rods coming apart from the crankshaft, severely damaging the engine block and cylinder bore.
It goes without saying that if the car engine has bad rod bearings, simply stop driving and have the engine rebuilt right away.
How Often Should You Change The Rod Bearing
Internal engine parts like the rod bearings don’t have a schedule for routine maintenance. When rebuilding an engine, you will only change the ball bearings for preventative reasons, but in case your engine knocks at the bottom or is losing oil pressure, the problem could be with the rod bearings.
Your vehicle’s engine is more susceptible to damage if you take too long and put off replacing the rod bearings. Rod bearing replacement versus engine replacement will involve changing the rod bearings as soon as you notice any sign of trouble.
Bad Rod Bearing Symptoms
If your rod bearing needs changing, you might find either one or a couple of the following symptoms of rod knock:
- Engine roar. A knocking sound from inside the engine is the most typical symptom.
- A decrease in the pressure of oil. Too much bearing wear may cause a drop in oil pressure.
- Transmitter noise: The crank turns counterclockwise or dirt that clogs the oil pump are two potential sources of transmission noise.
- Worn-out belts: rod journals may cause the belts to wear unevenly if they advance too far.
Maintenance-Related Services
A great time to look for unusual wear on other engine components is when you replace a rod bearing. These elements comprise:
- Pistons
- Timing links
- Crankshaft
- Bearings
- Seals
- Gaskets
- Bolts on the cylinder head
Rod Knock Symptoms
There are a few symptoms of rod knock that can be used to identify a rod knock, just like with any other system component in your car. The following are these signs:
Symptoms Of Rod Knock #1 – A Knocking Noise
One of the symptoms of rod knock is undoubtedly a knocking noise. When you first start the car, you’ll probably hear this loud banging.
As you put more weight on your car or depress the accelerator, it will also rise.
Symptoms Of Rod Knock #2 – Reduced Oil Pressure
Lower oil pressure than usual may be present when a bearing has failed or is about to fail. When the car first starts up, it’s the most obvious.
You might even get a warning about the pressure with the check oil pressure warning light on your dash. After a few minutes, if the light goes out and the pressure returns to normal, this is a clear sign that a bearing has failed.
Fixing A Rod Knock
The only fix is rebuilding the engine which involves removing the rods and then swapping out the bearings. The crank needs polishing and likely turning because there may be damage surface of the crank journal.
To remove any surface dings, they will turn the crank journal, on which the rod bearing will ride, by grinding it down, reducing the journal’s diameter. Here, phrases like “10 under” are used.
You can only turn the crank so many times before it is only useful for making a lamp or yard art. A crank must turn before running much thicker bearings that correspond to the crank’s turn quantity.
While you’re at it, you may as well swap out the main bearings of the crank and try to determine if the failure of the rod bearing was due to something you could control, like a malfunctioning oil pump.
Engine Knocking Causes
Engine knocking could occur for several reasons:
Symptoms Of Rod Knock, Causes #1: Low-Octane Or Subpar Fuel
The mixture of fuel and air may detonate early and produce a detonation knock if gas has a low octane content. A knocking or pinging noise is the result.
As per the octane rating of each fuel type, they receive names and numbers.
The fuel is refined and has a higher octane percentage the higher the octane rating. It has less chance of igniting too soon because of the more organized detonation.
Manufacturers using both numbers and names will often refer to octane levels: Bronze or Regular is 87% octane, Silver or Extra is 89%, and Premium, Gold, or Supreme is between 91% and 93%. You can also frequently access Octane 85 in regions with higher elevations.
Symptoms Of Rod Knock, Causes #2: Defective Spark Plugs
To ignite the mixture of fuel and air for the engine’s power stroke, spark plugs create the “spark” inside each combustion chamber. Engine knocking may come about due to faulty or improper plugs, as well as incorrect spacing.
Detonation knock, or premature detonation, can be due to spark plugs because they have different levels of heat tolerances. A spark that is weak or doesn’t cause the mixture to ignite will occur in a gap that is either too narrow or too wide.
In modern vehicles, the car’s computer controls the spark plug that ignites the mixture of fuel and air. It is activated via the distributor cap in older automobiles.
The ignition timing inside the combustion chamber can be off with defective or improper plugs, which can also cause knocking.
Symptoms Of Rod Knock, Causes #3: A Bad Knock Detector
Sensors and microcomputers are used in modern vehicles to maintain smooth engine operation. The timing, mixture of fuel and air, and fuel injectors are all under the control of the engine control unit (ECU).
The knock sensor notifies the ECU and then initiates a problem-solving process if there is any knocking. You might hear knocking, though, if the knock sensor is faulty.
Symptoms Of Rod Knock, Causes #4: A Fuel Lean Air Mixture
A spark that ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture causes combustion to happen. A lean mixture of fuel and air results from having too much oxygen present.
This indicates that there isn’t enough fuel present to quickly burn, which causes several detonations as well as a knocking noise. The cylinder walls and pistons will sustain damage if you do not address the issue quickly.
The usual causes relate to engine parts that regulate and control both fuel and airflow. Verify the fuel injectors as well as the pump are in good working order and check the oxygen and mass airflow sensors.
Symptoms Of Rod Knock, Causes #5: Rusted Bearings
When a vehicle whether it’s that Audi or VW golf is running at 1500 RPM, the rotation is roughly 90,000 times in an hour. Driving an hour to and from work five days each week results in 900,000 rotations; press the pedal and increase that number to anywhere from 3000 to 5000RPM or even more, and the weekly total increases.
The engine can perform 50 million rotations over a year, which can lead to bearing wear.
The connecting rod bearings and the main bearings that are between the connecting rod as well as the engine block both undergo millions of rotations each. As bearings deteriorate over time, the engine may start to rattle or knock. It can harm connecting rods if left unchecked.
Symptoms Of Rod Knock, Causes #6: Timing Belt Or Chain Problems
The crankshaft and camshaft connect via a timing belt or chain. This also synchronizes the piston movement with both the opening as well as the closing of the intake and exhaust valves.
In case the timing is not correct, the spark will not occur when it should, causing multiple explosions that cause the engine to knock.
Some older or classic cars will have a distributor cap, that is also connected with the timing to make sure the spark plug receives the electrical charge at the right timing that is needed to ignite the mixture of fuel and air at the proper time.
Instead, modern engines use computer controls to precisely time the spark to occur during the compression cycle of the piston of the mixture of fuel and air. In newer vehicles, incorrect combustion timing could be caused by a malfunctioning of the computer as opposed to a mechanical issue as in older vehicles.
Symptoms Of Rod Knock, Causes #7: Inadequate Lubrication Of Cylinder Head
In case the cylinder head doesn’t get enough lubrication, you will hear a knocking noise. When there is not enough oil inside the reservoir pan due to leaks or old oil, this frequently happens.
Generic oils with a much lower flashpoint can contribute to rod knock. This is because they will evaporate when they reach the upper cylinder walls as a result of high temperatures.
To ensure the cylinder head has enough lubrication oil, many manufacturers advise using synthetic oil. Piston ring damage and a shellac-like finish on the walls of the cylinder can both result from insufficient lubrication. Power, compression, and efficiencies may all suffer as a result.
Symptoms Of Rod Knock, Causes #8: Reduced Oil Pressure
Engine knock can also result from lowered oil pressure. Oil lubricates moving components like the cam lobes, camshaft, lifters, valve stems, as well as rocker arms while also dissipating heat from them.
Oil is then added to the lash, or the space between components, to fill and lubricate any gaps. The components clang or knock when the gaps widen as a result of low oil pressure or wear.
Before the oil reaches every gap in the engine, the sound of knocking could be more audible during cold starts.
Modern engines utilize hydraulic lifters that help reduce lash and thereby knock, so low oil pressure also affects these engines. Low-quality oils may thin at high engine temperatures, which can obstruct the formation of the right oil pressure.
If there is a leak inside the oil system, using the engine oil the manufacturer recommends should result in the proper oil pressure.
Check for oil that is on the ground directly under the engine. You could also check around the seals and see if there is a leaking of oil. You may also want to inspect the spark plugs for white ash. In addition, the bluish-black exhaust indicates that oil is probably burning inside the combustion chambers.
Symptoms Of Rod Knock, Causes #9: Valve Lifter Defect
No matter how hot or how cold the engine is, defective valve lifters make a fast-tapping noise. Valve lifters or hydraulic tappets maintain the engine’s valve clearance at zero.
In opposition to the valve stem they support, they are set at the tip of each push arm.
Over the sound of the engine, a stuck lifter may make a ticking, clicking, or tapping noise. How loud and long they often indicate the seriousness of the issue.
At startup, dirty oil frequently results in clicking for a short period. The engine’s lifter valve will deteriorate if the noise doesn’t stop.
Symptoms Of Rod Knock, Causes #10: Carbon Deposits
Even with detergents or additives that remove carbon, carbon buildup can still occur in carbon-based fuels like gasoline and diesel.
The combustion chamber, cylinder walls, pistons, valves, spark plugs, and valve seats may all develop carbon buildup. The buildup will decrease the volume in the chamber, heightens compression, and lessens the power stroke’s effectiveness.
In addition, carbon deposits might produce hotspots that could ignite the mixture of air and fuel before the spark plug. A shockwave forms when the piston gets to the top of the stroke. This is due to the slightly out-of-phase double firings in the chamber.
A rattle, ping, or knock that resembles a can that is full of marbles is the end result. The outcomes are the same if the spark plug lights up the mixture first and then the hotspot detonation.
In contemporary vehicles, a knock sensor will identify engine knocks and then transmit the information to the ECU. The ECU modifies timing to correspond with the extra firing from the carbon. The adjustment will guards against significant harm to the engine. Performance and efficiency, unfortunately, suffer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Rod Knock
Rod knock occurs when one or more of your rods knock on the crank as it rotates in a different direction. The connecting rod, which we’ll refer to as the rod from now on, is attached to the crank, and between the two is a bearing made of a material that is softer than the rod or the crank.
What Causes Rod Knock
An engine noise that sounds like deep rapping is called a rod knock. Wear or damage are the root causes. Movement is hampered by excessive clearance between connecting rods inside bearings in a vehicle. Metal strikes metal and makes a knocking sound when the piston shifts in direction.
What Does A Rod Knock Sound Like
Knocking noises: A knocking noise is the most typical sign of rod knock. When you turn on your car, you will hear a banging or knocking sound (as if someone is banging metal against your iron door) if a rod knock is installed. As you press the gas pedal, the loudness will grow.